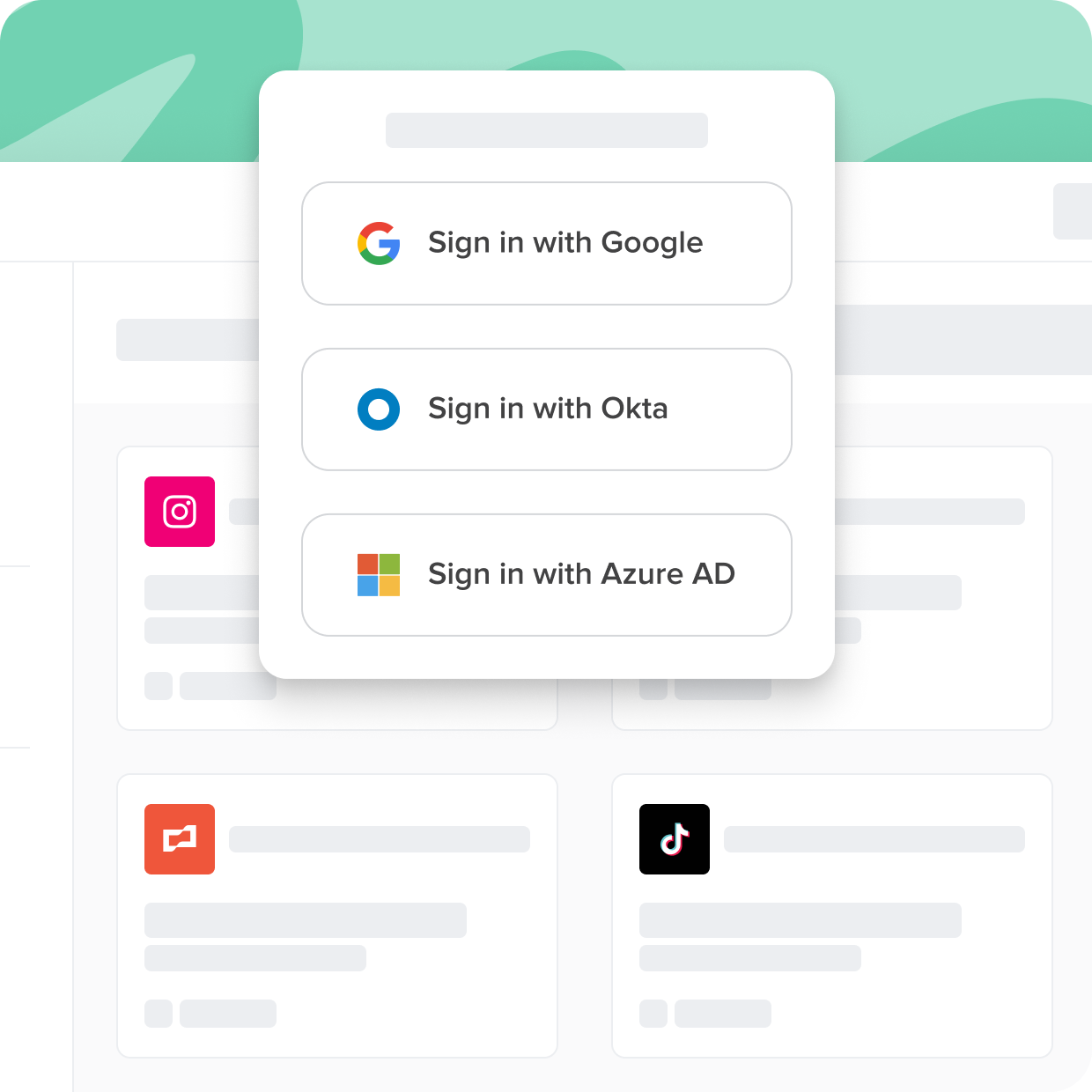
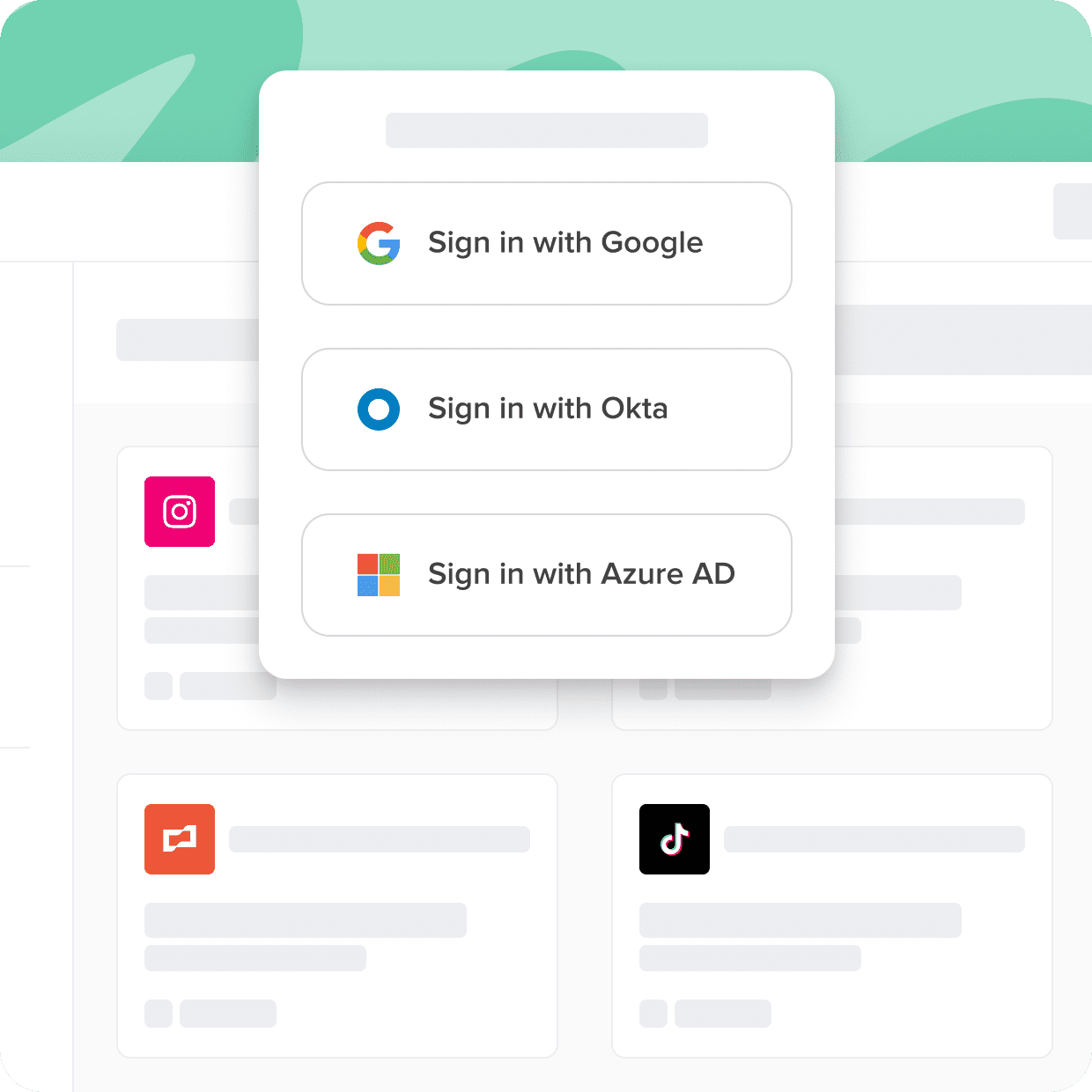
Access management in cybersecurity focuses on controlling user access to resources, while Single Sign-On (SSO) simplifies authentication by allowing users to log in once and access multiple applications without needing to authenticate separately for each one.
Unfortunately, many corporate applications don't support the SSO standard and can't reap all the benefits. The applications that fall into this category are best called "nonfederated." Nonfederated applications are a new category that is becoming increasingly challenging for businesses to manage and secure effectively, yet increasingly critical for businesses to succeed.
Cerby connects all of your apps to your SSO tools, even if they don't support the SSO standard. In this guide, you'll learn about SSO software, the history, and the benefits.
Streamline Access With Single Sign-on
Not all apps are created equal. Some come with security gaps and complexities that can hinder user adoption and put sensitive data at risk. With Cerby, you can ensure secure and seamless access to all your applications, regardless of their support for standards like SSO.
With Cerby You Can

Close the Identity Gap
Universally Enforce 2FA

Eliminate The SSO Tax
Access Management In Cyber Security
There is a growing emphasis on cyber security and access controls in the business world today. Organizations can protect their data and digital assets more effectively with the right tools and procedures. This often results in improved business outcomes and greater efficiency across the board. But what is access management? More specifically, what is access management in cyber security?At its core, access management is about defining and regulating user access to digital resources. This includes determining who should have access to specific information or systems and ensuring that they can only access the resources necessary for their respective roles. Access management goes beyond merely securing passwords, it encompasses the entire process of granting, updating, and revoking access permissions. This is emphasized in the Ponemon Institute’s study, stating that many organizations are unable to reduce the cybersecurity risks that are caused by shared accounts and 50% of organizations’ access management strategy enables employees to share logins. However, only 27% are actually effective in reducing cybersecurity risks.
Access management in cyber security, by extension, is an essential component of information security centered around the management of user identities, authentication, and authorization. It involves implementing the necessary policies and procedures to make sure that only authorized parties have access to sensitive information. By controlling who has access to what data, organizations can mitigate risk on a large scale.
To better understand the identity and access management process, it’s important to consider its key elements, which are as follows:
- Identity management: This is the process of creating, maintaining, and verifying unique user identities.
- Authentication: Authentication is the means by which user identities are verified when attempting to access a system or resource.
- Authorization: This is the process of determining what level of access a user should have to specific resources based on their identity and role.
- Auditing and monitoring: Auditing and monitoring involves tracking and reviewing user access to resources, detecting suspicious activity, and generating reports.
It’s important for all organizations to become familiar with the various components of access management in order to ensure security and compliance with all relevant standards.
Identity And Access Management
Identity and access management (IAM) is a comprehensive framework designed to manage user identities and control access to an organization's resources. The main goal of identity management is to ensure that the right individuals have access to the right resources at the right time. The significance of IAM security lies in its ability to protect sensitive data, maintain compliance, and reduce the risk of security breaches.
By implementing an effective IAM framework, organizations can:
Protect sensitive information by controlling access and reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Maintain compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Improve operational efficiency by streamlining user management and access control processes.
Enhance security posture by minimizing insider threats and detecting suspicious activities.
With the number of people on the internet today, access management has become a critical process for safeguarding sensitive data. Hackers and other deceitful parties are developing increasingly advanced techniques to gain access to private information. As a result, businesses need to up their game to ensure maximum security and remain compliant with applicable regulations.
Privileged Access Management
Privileged access management (PAM) is a specialized area of IAM that focuses on the control and monitoring of privileged accounts. These accounts have elevated access rights to sensitive data and critical systems, making them an attractive target for cybercriminals. PAM solutions help mitigate this risk by providing a robust framework for managing privileged accounts.The benefits of privileged access management solutions include:
Enhanced security: PAM solutions provide robust security controls to protect privileged accounts. Privileged access management CyberArk tools are great examples of this.
Compliance: Another key advantage of PAM solutions is that they help organizations maintain compliance by providing comprehensive auditing and reporting capabilities.
- Efficient administration: PAM solutions streamline the management of privileged accounts by automating processes such as password rotation and access provisioning.
- Insider threat mitigation: By closely controlling access, privileged access management software helps organizations detect and prevent insider threats.
- Reduced attack surface: PAM solutions reduce attack surfaces by limiting the number of privileged accounts, enforcing least privilege, and implementing strong authentication and access controls.
Different privileged access management vendors offer different tools and software, so it’s important for businesses to do their research before settling on a solution. For instance, privileged access management Azure tools may be best suited for those already working in an Azure environment.
Access Management Tools
Access management software plays a crucial role in securing digital assets and ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive information. There are various access management tools and solutions available on the market, each catering to diverse organizational needs. They include commercial, open-source, and cloud-based options.Here are some of the most popular identity and access management tools available today:
- Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
- Okta
- OneLogin
- IBM Security Identity and Access Assurance
- Keycloak
- FreeIPA
- WSO2 Identity Server
- OpenIAM
- Gluu Server
- Shibboleth
- CAS (Central Authentication Service)
These lists highlight some of the most popular solutions in use in today’s digital landscape. When evaluating identity and access management tools, organizations should consider factors such as scalability, ease of integration, and support for various authentication methods. By selecting the right access management software, organizations can effectively manage user access and maintain regulatory compliance.
Identity And Access Management Azure
Implementing identity and access management in cloud computing can be complex due to the nature of the cloud itself. Challenges of implementing access management in cloud environments include:- A distributed and dynamic nature: Cloud environments often involve a large number of distributed resources and services, which make it difficult to manage user access consistently across all components.
- Multi-tenancy: In many cases, cloud platforms serve multiple organizations or tenants. This can be challenging to ensure proper isolation and access control between them.
- Scalability: Cloud environments are designed to scale rapidly, posing challenges in managing user access and permissions effectively, especially as the number of users and resources grows.
- Use a centralized IAM solution: A centralized IAM solution, such as an identity and access management Azure tool, can streamline access management across all cloud resources and services.
- Implement the principle of least privilege: Limit user access rights to the minimum necessary to perform their job functions. This minimizes the potential damage in case of unauthorized access or security breaches.
- Deploy strong authentication methods: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that users are who they claim to be
Identity And Access Management Jobs
The job market for access management professionals has experienced significant growth in recent years, fueled by the increasing demand for robust security measures. As cyber threats evolve, more identity and access management jobs are likely to pop up on the market. This presents an excellent opportunity for those considering entering the field.
Access management professionals can fill a variety of roles. Common positions include IAM analyst and IAM architect. Their responsibilities typically involve designing, implementing, and maintaining the identity and access management systems; developing and enforcing access control policies; and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. Access management professionals may also be required to provide guidance on IAM best practices.
The salary for access management professionals varies depending on the role in question, as well as experience and geographic location. Entry-level roles generally command lower salaries than more experienced positions. Cyber security IAM salary details also depend on factors such as the size of the organization and the complexity of the IAM infrastructure. Professionals working in large organizations or highly regulated industries may receive higher salaries.
Researching identity and access to management analyst salary information, as well as the salaries of related positions, is crucial for job-seekers. This will give them a better idea of what to expect in any given role.
Identity And Access Management Solutions
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, organizations must adopt innovative approaches and leverage new technologies to ensure the security and integrity of their digital assets. Emerging trends are shaping identity and access management solutions, driving the development of user management solutions that provide enhanced security and ease of use.
One of the key trends in the IAM domain is the growing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. These technologies enable the creation of advanced access management tools that can analyze vast amounts of data and detect anomalies in real-time. AI- and ML-powered IAM cyber security tools can automatically adapt access policies based on user behavior and risk factors.
Another major trend is the increasing emphasis on zero trust security models. The zero trust approach assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default. It requires continuous validation of their identities and permissions before granting access to resources. The top identity and access management tools are incorporating zero trust principles to improve security.