An access management system is a set of tools and rules, and an added layer to SSO, that helps organizations control who can access their systems and resources. It ensures that only authorized individuals can access the right information at the right time while keeping unauthorized users out.
Unfortunately, many corporate applications don't support the SSO standard and can't reap all the benefits. The applications that fall into this category are best called "nonfederated." Nonfederated applications are a new category that is becoming increasingly challenging for businesses to manage and secure effectively, yet increasingly critical for businesses to succeed.
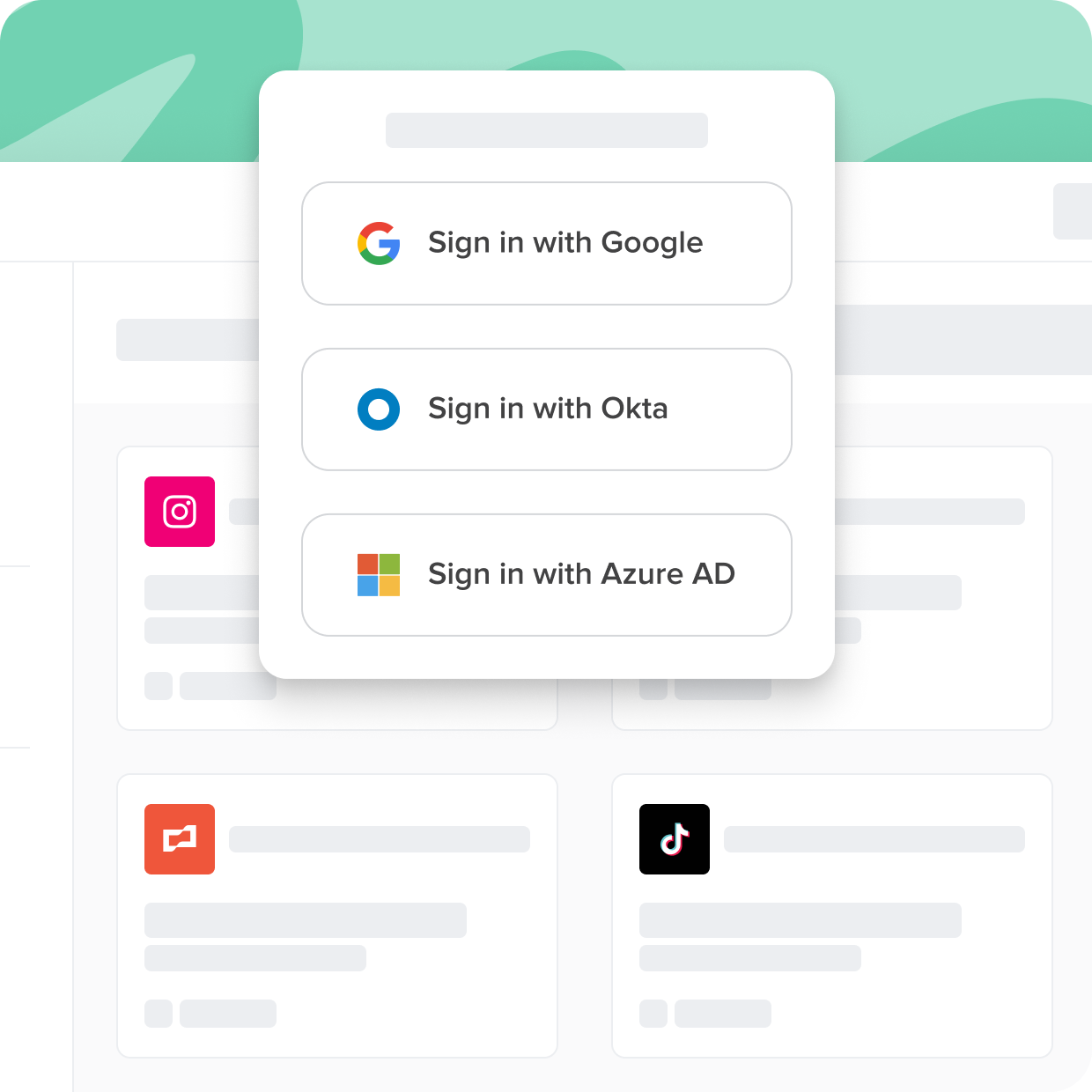
Cerby connects all of your apps to your SSO tools, even if they don't support the SSO standard. In this guide, you'll learn about SSO software, the history, and the benefits.
Streamline Access With Single Sign-On
Not all apps are created equal. Some come with security gaps and complexities that can hinder user adoption and put sensitive data at risk. With Cerby, you can ensure secure and seamless access to all your applications, regardless of their support for standards like SSO.
With Cerby You Can

Close the identity gap
Universally enforce 2FA

Eliminate the SSO tax
Access Management System
In today's interconnected, digital world, businesses encounter numerous challenges related to information security and proper data governance, and those challenges will only increase as technology becomes more advanced. One of the most critical aspects of securing sensitive information is ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to it. This is where a robust access management system can make a difference. An access management system is a helpful technology solution that can manage and control levels of access to a company’s digital assets, including applications, networks, and databases.
As more businesses find new ways of aggregating valuable data, user access management tools have become an integral part of organizations’ security infrastructures. These tools are engineered to control and monitor access to critical data and thwart unauthorized access by both internal and external users. They can also help ensure compliance with data governance regulations and reduce the risk of other cyber threats like data breaches, cyber-attacks, and other nefarious cyber activity.
Privileged access management (PAM) is another invaluable aspect of access management initiatives. Generally speaking, PAM refers to the process of managing and controlling access to sensitive systems and data by privileged users – such as IT staff and/or system administrators. PAM solutions provide an added layer of security by monitoring privileged user activities, enforcing strict access policies, and detecting and mitigating other threats to security.
The growing significance of access management systems can be linked to a handful of contributing factors. Firstly, as more companies are hiring remote workers and utilizing cloud-based solutions, it has become more difficult to maintain a secure network perimeter. There’s also the rise of cyber-attacks and data breaches which have underscored the urgency for implementing tighter security measures. And finally, data governance regulations like GDPR and CCPA have made it a requirement by law for businesses to ensure data privacy and protection. This is all emphasized in the Ponemon Institute’s study, steps should be taken to track applications and secure them as part of the organization’s identity and access management strategy.
With user access management tools and privileged access management solutions, businesses can better protect their sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. And as technology continues to advance and evolve, access management will continue to play an important role in securing digital assets and thwarting nefarious cyber activities. anagement system
What Is Identity And Access Management
We’ve already touched on some of the basics of access management, but exactly what is identity and access management (IAM)? Identity access management refers to the process of managing and controlling who has access to various digital resources based on a user’s identity. It involves the integration of numerous technologies and processes to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to specific data and/or applications. Or, in other words, IAM can help organizations establish user identities and determine what resources they can access, and monitor user actions.
Modern IAM architecture generally involves the utilization of a centralized system that can manage user identities and access permissions. These systems can provide a single source of truth for user data, which enables organizations to easily manage user access across a multitude of applications and systems. The data access management system also gives organizations the power to assign appropriate access rights to users based on their roles and responsibilities and monitor their activities in order to detect and prevent unauthorized access.
Another critical aspect of IAM is data access governance, which refers to the process of creating and enforcing policies and procedures that dictate data access parameters. These policies typically include rules for user authentication, password management, and data encryption. Data access governance also ensures that sensitive information remains protected, and all relevant compliance requirements are met.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) utilizes its innovative AWS IAM system design to provide a centralized control panel for any managing user attempting to access AWS resources, including Amazon S3, Amazon EC2, and Amazon RDS. AWS IAM system design helps organizations assign granular permissions to individual users or groups of users to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to certain resources. It also empowers the organization to closely monitor user activity and detect any potential security weaknesses.
IAM is crucial for many different businesses, but especially those that rely heavily on digital resources for successful operations. And in highly regulated industries such as finance and healthcare, IAM helps protect confidential information like medical histories and financial data.
Identity And Access Management In Cyber Security
Because identity and access management can help businesses manage user identities and access permissions across different systems, applications, and devices, it also plays an invaluable role in cybersecurity infrastructures. With a robust IAM system in place, business organizations can monitor and control user access, detect and prevent unauthorized access, and maintain compliance with data privacy regulations.
Within the context of SaaS companies, identity, and access management in cyber security is critical. SaaS (software as a service) companies provide cloud-based services to their clients, which means that client data is stored remotely and accessed via the Internet. This creates a number of security challenges that require effective IAM solutions to help protect against cyber-attacks and data breaches.
User access management is an important aspect of IAM, especially for SaaS companies. User access management involves managing user identities, authentication, and authorization to ensure that unauthorized users cannot gain access to specific, sensitive data. User access management examples might include things like multi-step authentication, role-based access control, and granular permissions, among others. These measures help prevent unauthorized access and safeguard against potential security threats.
User access management best practices for SaaS companies include implementing rigorous password policies, utilizing multi-factor authentication, and consistently reviewing access permissions to ensure that they are up-to-date and that there are no weak links in the chain of protective measures. It’s also vital for organizations to continually monitor user activity and detect any suspicious behavior, which could include things like repeated failed login attempts or abnormal access patterns.
Access Management Process
The process of engineering, constructing, and implementing an access management process for businesses both small and large is a multi-step process. These steps generally include defining a user access management policy, identifying user access management roles and responsibilities, selecting a user access management system, implementing user access management controls, and finally testing the entire user access management process.
The first step in designing an access management process is defining a user access management policy. This policy would ideally outline the organization’s approach to user access management, including the types of data and applications that users have permission to access, the roles and responsibilities of those different users, and the process for granting and revoking permissions and/or access.
Next, businesses must identify user access management roles and responsibilities. This involves identifying the different user roles within an organization and defining access permissions for each unique role. It is essential that access permissions are congruent to job responsibilities to prevent unauthorized access. Or, to put it another way – a business wouldn’t want a new intern to have the highest level of access.
Thirdly, the organization must create an access management process that defines the steps involved in granting and revoking access (including the approval process, user authentication, and access control measures). Access management should also be well-documented, communicated clearly and concisely to all relevant stakeholders, and regularly reviewed to ensure effectiveness.
After that, businesses must implement user access management controls, which involve configuring the entire user access management system to enforce various access controls. And finally, testing the user access management process can provide valuable information about which user access management controls are working effectively and where any weaknesses or vulnerabilities remain. Businesses must regularly conduct security audits to identify areas for improvement and ensure the integrity of the user access management process. Identity and access management tools
Identity And Access Management Tools
Identity and access management tools are essential solutions for business organizations seeking to manage user access and security measures. Here are some examples of the top identity and access management tools and their various use cases:- OpenIAM: This open-source IAM solution offers identity and access management for on-premise and cloud applications alike, in addition to user provisioning and self-service password management services.
- Keycloak: Another great open-source IAM solution that provides identity and access management for both web and mobile applications.
- ForgeRock: This IAM solution supports single sign-on, multi-factor authentication, as well as user provisioning.
- OneLogin: OneLogin offers secure access to cloud and on-premise applications, in addition to multi-step authentication and directory integration. It also provides role-based access controls and user provisioning.
- Microsoft Azure Active Directory: This cloud-based IAM solution allows for identity and access management for Microsoft Office 365, Azure, and other useful cloud services. It can support single sign-on, multi-factor authentication, and user provisioning.
Simply put identity, and access management solutions are invaluable solutions for business organizations to enhance their data security, and these IAM tools examples can show just how useful they can be for businesses. Identity management tools are suitable for many different use cases, such as secure access to cloud and web applications, on-premise applications, mobile devices, and even IoT devices.
Organizations should seek to implement the IAM tool that best aligns with their specific needs and requirements.